Have you recently seen or heard the term “roaming” either from your cell phone carrier or your phone’s settings? If you did so and are confused by this term, don’t worry, as I will explain what it is and how it works. The explanation will be very simple so even a five-year-old can understand it.
What does roaming mean on phone?
So to begin with, what exactly does data roaming mean? In wireless telecommunications, your cellular devices start roaming around when you go outside of your carrier’s coverage area. Your device will start to roam and search for other cell phone towers and will try to connect with them.
These towers will usually belong to your carrier’s competitors or other cell phone providers who have agreed with your carrier to let you connect to their towers. Since these towers do not belong to your carrier, depending on your plan, you will be heavily charged for making a text, call, or using data through the tower.
Types of roaming
Because international roaming is the most popular type of roaming, people often forget that carriers classify roaming in two types of ways: Domestic roaming and international roaming.
International roaming:
International roaming, as its name suggests, is when you use your phone outside of the country. For example, if you have T-Mobile and you use your device while traveling to Canada or Mexico, this would be considered international roaming.
International roaming is often more expensive than domestic because your carrier has to make agreements with foreign companies/carriers in order for you to use their towers.
Domestic roaming:
The other type of roaming is domestic roaming. Domestic roaming occurs when you go out of your carrier’s coverage area and your phone connects to another tower that does not belong to your carrier. The biggest difference is that although you are out of your carrier’s coverage area, you’re not out of the country.
The other big difference is that domestic roaming is usually free. Since no coverage makes the carrier looks bad, they often do not charge for domestic roaming.
While domestic roaming is usually free, you should be extremely careful when using it. Since roaming costs the carrier money, your carrier will terminate your account without any way of porting out your number if they determine that you’ve used excessive roaming. It’s best to consult with your carrier’s agreement to be sure of how much roaming you’re allowed to use.
Should data roaming be on or off?
Having data roaming on or off depends on your situation.
If you are not going out of the country, it is more beneficial to have Data roaming on. This is because most carriers won’t mind if you reasonably use domestic roaming.
For example, if for any reason you have to go to an isolated part of your town, you will not lose coverage if your data roaming is on.
Now, data roaming should be turned off if you’re traveling out of the country. Since most carriers charge hefty fees for international roaming, you should instead get a local SIM card.
But first, check your carrier’s agreement and check if they offer free or limited international roaming as carriers like AT&T and T-Mobile currently do with certain plans.
How to avoid roaming charges
If your carrier has high roaming fees, the best thing you can do to avoid those charges is to turn off roaming directly from your cell phone. Whether you have a Samsung, iPhone, or any Android device, disabling roaming is simple.
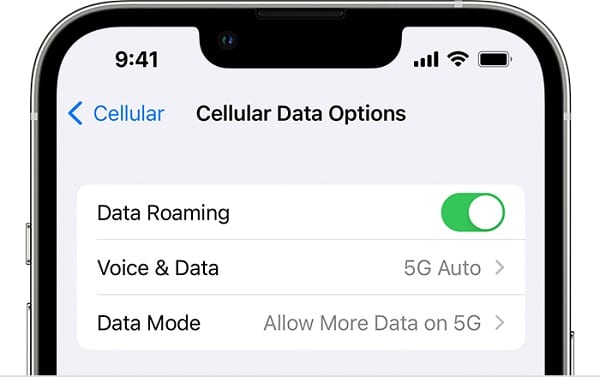
Turn off data roaming iPhone
Turning off roaming on iPhone is as simple as it could get:
- From your home screen, tap Settings.
- Tap Cellular.
- Now tap Cellular Data Options.
- Toggle off Data Roaming.
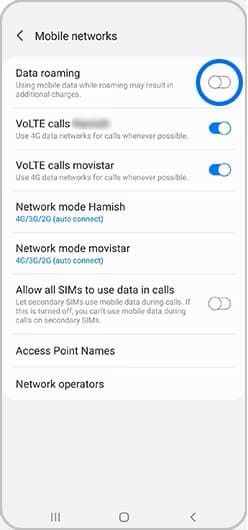
How to turn off data roaming on Samsung, Android
Disabling data roaming on Android or Samsung devices is a similar procedure as on iPhone.
- From your home screen, tap Settings> Connections> Mobile networks.
- From the Mobile network page, toggle the Data roaming button.